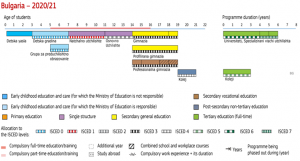
Bulgarian educational system
Stages of the Education System
Early Childhood Education and Care
Early childhood education and care is managed by local authorities, and is not part of the State’s responsibilities, between the ages of 0 – 3. Between the ages of 3 – 6/7 it becomes part of the responsibilities of the Ministry of Education and Science.
Kindergartens are institutions within the pre-school and school education system for raising, education, and socialization of children from age of 3 up to the age of 7 (entering first class) in line with the state pre-school education standard. Children aged 2 can also enter kindergarten in line with the conditions and rules of the Law on Pre-School and School Education.
Kindergartens are municipal or private. Public kindergartens can be opened as an exception to the Ministry of Defense or on the grounds of an international treaty. Kindergartens to the Ministry of defense are aimed to raising, education and socialization of children of military and civil personnel of the Ministry.
Central kindergarten is a municipal kindergarten, which is situated in the closest settlement of the municipality or a neighboring municipality, where children from the settlements with no kindergarten or a school providing mandatory pre-school education are raised, educated, and socialized.
Education and training of children in kindergartens is organized and provided in line with the Pre-school Education State Standard. School readiness is assessed at the end of pre-school education stage by comparing acquired learning outcomes with the learning outcomes described in the standards. School readiness certificate is issued.
Pre-school education is included in the National Qualifications Framework of the Republic of Bulgaria, which was adopted by Council of Ministers’ Decision No 96/2002. In this level knowledge, skills and competences (self-dependence and responsibility, and communicative and social competences).
School Education
School education is mandatory from age of 7 on or from age of 6 according to parents’ assessment to age of 16. It provides for education and up-bringing of students according to their individual needs and in line with the requirements and expectations for a successful realization in civic society.
The school is an institution in the system of pre-school and school education, which train, educate and socialize students and provide the conditions for the completion of grade and stage and / or to acquire education. As specified in the Law on pre-school and school education cases, the school provides conditions for acquisition of a vocational qualification.
Schools may provide compulsory preschool education of children in the terms and conditions of state educational standards for pre-school education and state educational standard for physical environment and information and library provision of kindergartens, schools and centers of support for personal development.
Schools are state, municipal, private or religious. According to the type of training schools are non-specialized and specialized.
According stage or level of education non-specialized schools are:
- primary (I – IV class inclusive);
- main (I – VII class inclusive);
- schools (VIII – XII class inclusive);
- united (I – X including class);
- secondary (I – XII class inclusive).
Higher Education
The Republic of Bulgaria is also among the first countries which signed in 1999 in Bologna the Joint Declaration for European Higher Education Area.
The higher education governance is performed at state and institutional level. The state is responsible for the development and the implementation of a long-term national policy and establishment of conditions, which guarantee the academic autonomy of higher education institutions, the quality of education, and the provision of adequate conditions for performing scientific research.
The institutional management is performed according to the rights for an academic autonomy of the higher education institutions, but the state assists for development of modern institutional governance through distribution of resources on a competitive basis. Bulgaria works actively towards building up of a favorable environment for modernization of higher education, in line with the needs of the society and of the business. Good practices are studied and multiplied. Possibilities for introduction of new models, which are related to application of modern approaches for institutional governance leading to better financial management, are studied.
Adult Education
Adult education is a priority and takes many forms, ranging from formal class-based learning to self-directed and e-learning. Local authorities are responsible for framing adult education policies for their respective regions. Adult education is most often provided by Licensed Vocational Training centers, as well as Trade Unions.For a brief description of the different levels of the education system and other related topics such as teachers and special needs education, please read the Organisation and Governance and of each educational level: Early Childhood Education, Integrated Primary and Lower Secondary Education, Upper Secondary Education and Post Secondary Non Tertiary Education, Higher Education and Adult Education and Training
For a brief description of other main topics regarding the national education system, please read the introduction article of Funding education, Teachers and education staff, Management and other educational staff, Educational support and guidance, Quality assurance, Mobility and internationalisation
For information on recently adopted or planned reforms and policy measures, please consult topic Ongoing Reforms and Policy Developments
While Eurypedia provides comprehensive and comparable information, further information may also be found on the websites of the Ministry of Education and Science, as well as that of the National Statistical Institute.