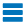
Distance Calculation with Ultrasonic Sensor
How Deep is the Ocean?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7fY2EOIjeBE
This activity is a continuation of an earlier activity we did this year with an infrared sensor. It came out of an idea of one of our students for making a safety device. We discussed and investgated the matter and we started with a prototype application with an infrared sensor.
Summary
In this activity, students learn about how ultrasonic sensors work and identify where else in nature they are found. For example, bats and dolphins use ultrasound waves to estimate distance, to move and find their food. Students identify other uses of sonar such as mapping the seabed and measuring the depth of the ocean. They also build an application with an ultrasonic sensor and program the microbit to show the distance from an object on the LED matrix of the micro:bit. They also build a model of a car parking application.
Areas involded: Biology, Computer Science, Science and Technology.
Pre Required Knowledge
Basic programming, repetitions, if statements, variables.
The formula of the average speed
Electric power source, grounding, open and closed electric circuit
Learning objectives
With the completion of this activity, the students will be able to:
- Describe what is ultrasound and how ultrasonic sensors work.
- Identify other species that use ultrasound to communicate, move and find their food.
- Program an application with the micro:bit that uses an ultrasonic sensor.
- Provide a basic explanation of how sensors are integrated into robots via programming.
- Explain other uses of ultrasonic sensors such as measuring the ocean depth, mapping the seabed and car parking sensors.
An ultrasonic sensor generates sound waves to detect and measure the distance to objects.
In this project we have used an Ultrasonic Sensor to determine the distance of an obstacle from the sensor.
https://www.hackster.io/arbazhussain/distance-calculation-with-ultrasonic-sensor-26d63e
Bats use echolocation to find and identify objects in their surroundings.
Dolphins also use sonar to orient themselves, locate objects and determine object’s shape and size.
To help robots identify objects, engineers have created ultrasonic sensors that operate using the same principles.
Copyright © (left) Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources; (right)LEGO url
Copyright © Microsoft Education https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/education/oceans/lessons/measuring-ocean-depth/default.aspx
How does an Ultrasonic Distance Sensor work?
The Ultrasonic Sensor sends out a high-frequency sound pulse and then times how long it takes for the echo of the sound to reflect back. The sensor has 2 openings on its front. One opening transmits ultrasonic waves, (like a tiny speaker), the other receives them, (like a tiny microphone).
The speed of sound is approximately 341 meters (1100 feet) per second in air. The ultrasonic sensor uses this information along with the time difference between sending and receiving the sound pulse to determine the distance to an object. It uses the following mathematical equation:
Distance = Time x Speed of Sound divided by 2
Why/When to use Ultrasonic Sensors ?
- Ideally suited to accurate, automatic distance measurement in normal and difficult environments.
- Particularly suitable for environments where optical sensors are unusable such as smoke, dust and similar.
- Very accurate, stable and can be used over large ranges.
Ultrasonic sensors can measure the following parameters without contacting the medium to be measured:
- Distance
- Level
- Diameter
- Presence
- Position
Functioning Of Project:
The ultrasonic sensor emits a high-frequency sound pulse and calculates the distance depending upon the time taken by the echo signal to travel back after reflecting from the desired target. The speed of sound is 341 meters per second in air. After the distance is calculated, it will be displayed on the LED matrix of the micro:bit or an LCD display.
https://www.sparkfun.com/products/13959
We connected the Vcc to the 3V pin of the microbit, the Trig to Pin 0, the Echo to Pin 1 and the GND to the GND of the micro:bit.
https://www.instructables.com/id/Distance-Sensing-With-the-Microbit-and-Sonar-HC-SR/
If you run this code on the micro:bit and move your hand in front of the sensor you will see the distance on the LED matrix display of the micro:bit.
This project could be expanded to work as a prototype for a car parking alarm. Connect one speaker or one buzzer on Pin 0 and rearrange the ping and echo pins on pins 1 and 2 of the micro: bit. Then use pin 0 to produce tones more and more often as the distance decreases. Whenever your car comes near any object, the buzzer will ring and the LED will glow so that you don’t get your car damaged.
Ultrasound sensors were initially used in vehicles for detecting obstacles when parking but are now evolving into an automatic parking system.
Another idea is to make a device that will warn the cyclists if they are going too close to people or objects with their bike. The micro:bit can be programmed with the ultrasonic sensor so a grren LED will light when the distance is safe, a yellow LED when the bike is getting too close to an object or human and a red one if the bike is getting too close.
https://www.instructables.com/id/Distance-Sensing-With-the-Microbit-and-Sonar-HC-SR/
The same principle is used to calculate the water depth in the oceans. A transducer sends a sound pulse down into the water and picks up the reflected sound. The time it takes for the sound pulse to reach the bottom and return is measured precisely and the depth of the ocean is calculated by knowing how fast sound travels in the water (approximately 1,500meters per second).
https://dosits.org/people-and-sound/navigation/how-is-sound-used-to-measure-water-depth/
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/education/oceans/lessons/measuring-ocean-depth